
Fast and powerful cryptographic functions for Flutter.



---
[[Changelog]](./CHANGELOG.md) | [[License]](./LICENSE)
---
## About
The goal of this plugin is to provide a fast and powerful cryptographic functions by calling native libraries. On Android, it uses [javax.cypto](https://developer.android.com/reference/javax/crypto/package-summary), and on iOS, it uses [CommonCrypto](https://opensource.apple.com/source/CommonCrypto/) and [CryptoKit](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/cryptokit/)
I started this projet because I wanted to add cryptographic functions on a Flutter app. But I faced a problem with the well-known [Pointy Castle](https://pub.dev/packages/pointycastle) library: the performance was very poor. Here some benchmarks and comparison:
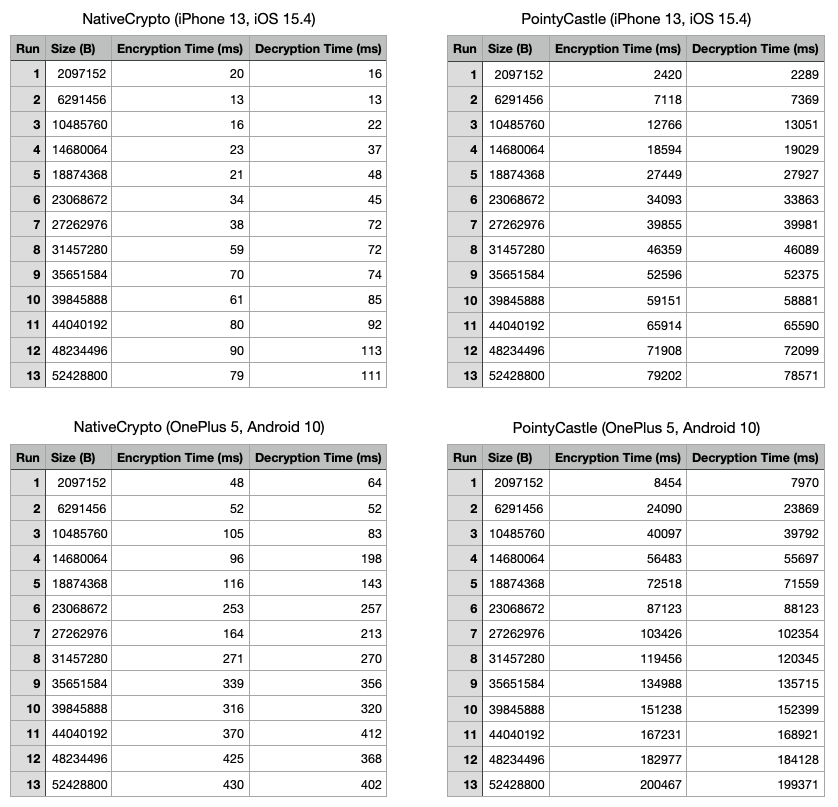
For comparison, on a *iPhone 13*, you can encrypt/decrypt a message of **2MiB** in **~5.6s** with PointyCastle and in **~40ms** with NativeCrypto. And on an *OnePlus 5*, you can encrypt/decrypt a message of **50MiB** in **~6min30** with PointyCastle and in less than **~1s** with NativeCrypto.
In short, NativeCrypto is incomparable with PointyCastle.
## Features
* Hash functions
- SHA-256
- SHA-384
- SHA-512
* HMAC functions
- HMAC-SHA-256
- HMAC-SHA-384
- HMAC-SHA-512
* Secure random
* PBKDF2
* AES
- Uint8List encryption/decryption
- File encryption/decryption
## Quick start
```dart
import 'package:native_crypto/native_crypto.dart';
Future main() async {
// Message to encrypt
final Uint8List message = 'Hello World!'.toBytes();
// Ask user for a password
final String password = await getPassword();
// Initialize a PBKDF2 object
final Pbkdf2 pbkdf2 = Pbkdf2(
length: 32, // 32 bytes
iterations: 1000,
salt: 'salt'.toBytes(),
hashAlgorithm: HashAlgorithm.sha256,
);
// Derive a secret key from the password
final SecretKey secretKey = await pbkdf2(password: password);
// Initialize an AES cipher
final AES cipher = AES(
key: secretKey,
mode: AESMode.gcm,
padding: AESPadding.none,
);
// Encrypt the message
final CipherText cipherText = await cipher.encrypt(message);
// Decrypt the message
final Uint8List decryptedMessage = await cipher.decrypt(cipherText);
// Verify and print the decrypted message
assert(listEquals(message, decryptedMessage));
print(decryptedMessage.toStr());
}
```
Check the [example](./native_crypto/example) for a complete example.
Please take a look a the compatibility table below to check if your target is supported.
> Note: This **Flutter** example must run on a real device or a simulator.
## Usage
#### Compatibility
First, check compatibility with your targets.
| iOS | Android | MacOS | Linux | Windows | Web |
| --- | ------- | ----- | ----- | ------- | --- |
| ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
> Warning: NativeCrypto 0.2.0+ is not compatible with lower NativeCrypto versions. Especially, with NativeCrypto 0.0. X because the cipher mode is not the same. Now, NativeCrypto uses AES-GCM mode instead of AES-CBC mode. (See [Changelog](./CHANGELOG.md))
NativeCrypto ciphertexts are formatted as follow:
```
+------------------+--------------------+------------------+
| Nonce (12 bytes) | Cipher text (n-28) | Tag (16 bytes) |
+------------------+--------------------+------------------+
```
> Warning: If your data comes from another source, make sur to use the same format.
#### Hash
To digest a message, you'll need to initialize a Hasher object implementing `Hash` . Then, you can digest your message.
```dart
Hash hasher = Sha256();
Uint8List digest = await hasher.digest(message);
```
> In NativeCrypto, you can use the following hash functions: SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512
#### HMAC
To generate a HMAC, you'll need to initialize a `Hmac` object. Then, you can generate a HMAC from a message and a secret key.
```dart
Hmac hmac = HmacSha256();
Uint8List hmac = await hmac.digest(message, secretKey);
```
> In NativeCrypto, you can use the following HMAC functions: HMAC-SHA-256, HMAC-SHA-384, HMAC-SHA-512
#### Keys
You can build a `SecretKey` from utf8, utf16, base64, base16 (hex) strings, int list or raw bytes. You can also generate a SecretKey from secure random.
```dart
SecretKey secretKey = SecretKey(bytes); // bytes is a Uint8List
SecretKey secretKey = SecretKey.fromUtf8('secret');
SecretKet secretKey = SecretKey.fromUtf16('secret');
SecretKey secretKey = SecretKey.fromBase64('c2VjcmV0');
SecretKey secretKey = SecretKey.fromBase16('63657274');
SecretKey secretKey = SecretKey.fromList([0x73, 0x65, 0x63, 0x72, 0x65, 0x74]);
SecretKey secretKey = await SecretKey.fromSecureRandom(32); // 32 bytes
```
#### Key derivation
You can derive a `SecretKey` using **PBKDF2**.
First, you need to initialize a `Pbkdf2` object.
```dart
final Pbkdf2 pbkdf2 = Pbkdf2(
length: 32, // 32 bytes
iterations: 1000,
salt: salt.toBytes(),
hashAlgorithm: HashAlgorithm.sha256,
);
```
Then, you can derive a `SecretKey` from a password.
```dart
SecretKey secretKey = await pbkdf2(password: password);
```
> Note: Pbkdf2 is a callable class. You can use it like a function.
#### Cipher
And now, you can use the `SecretKey` to encrypt/decrypt a message.
First, you need to initialize a `Cipher` object.
```dart
final AES cipher = AES(
key: key,
mode: AESMode.gcm,
padding: AESPadding.none,
);
```
Then, you can encrypt your message.
```dart
final CipherText cipherText = await cipher.encrypt(message);
```
After an encryption you obtain a `CipherText` which contains chunks. You can get the underlying bytes with `cipherText.bytes` .
Uppon receiving encrypted message `receivedData` , you can decrypt it.
You have to reconstruct the ciphertext and the setup the chunk factory.
```dart
final CipherText receivedCipherText CipherText(
receivedData,
chunkFactory: (bytes) => AESCipherChunk(
bytes,
ivLength: cipher.mode.ivLength,
tagLength: cipher.mode.tagLength,
),
),
```
Then, you can decrypt your message.
```dart
Uint8List message = await cipher.decrypt(receivedCipherText);
```
#### Files
You can encrypt/decrypt files.
First, you need to initialize a `Cipher` object.
```dart
final AES cipher = AES(
key: key,
mode: AESMode.gcm,
padding: AESPadding.none,
);
```
Then, you can encrypt your file.
```dart
await cipher.encryptFile(plainText, cipherText);
```
> Note: `plainText` and `cipherText` are `File` objects.
You can decrypt your file.
```dart
await cipher.decryptFile(cipherText, plainText);
```
#### Advanced
You can force the use of a specific IV. Please note that the IV must be unique for each encryption.
```dart
final CipherText cipherText = await cipher.encryptWithIV(message, iv);
```
⚠️ Use `encrypt(...)` instead of `encryptWithIV(...)` if you don't know what you are doing.
## Development
### Android
> https://docs.flutter.dev/development/packages-and-plugins/developing-packages#step-2b-add-android-platform-code-ktjava
* Launch Android Studio.
* Select Open an existing Android Studio Project in the Welcome to Android Studio dialog, or select File > Open from the menu, and select the `packages/native_crypto/example/android/build.gradle` file.
* In the Gradle Sync dialog, select OK.
* In the Android Gradle Plugin Update dialog, select Don’t remind me again for this project.
### iOS
> https://docs.flutter.dev/development/packages-and-plugins/developing-packages#step-2c-add-ios-platform-code-swifthm
* Launch Xcode.
* Select File > Open, and select the `packages/native_crypto/example/ios/Runner.xcworkspace` file.

